| [1] Ankrum J, Karp JM. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy: Two steps forward, one step back. Trends Mol Med. 2010;16(5): 203-209.
[2] Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, et al. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science. 1999; 284(5411):143-147.
[3] Phinney DG, Prockop DJ. Concise review: mesenchymal stem/multipotent stromal cells: the state of transdierentiation and modes of tissue repair-current views. Stem Cells. 2007; 25(11):2896-2902.
[4] Rando TA. Stem cells, ageing and the quest for immortality. Nature. 2006;441(7097):1080-1086.
[5] Chapel A, Bertho JM, Bensidhoum M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells home to injured tissues when co-infused with hematopoietic cells to treat a radiation-induced multi-organ failure syndrome. J Gene Med.2003;5(12):1028-1038.
[6] Chavakis E, Urbich C, Dimmeler S. Homing and engraftment of progenitor cells: a prerequisite for cell therapy. J Mol Cell Cardiol.2008;45(4):514-522.
[7] Barbash IM, Chouraqui P, Baron J, et al. Systemic delivery of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells to the infarcted myocardium: feasibility, cell migration, and body distribution.Circulation.2003;108(7):863-868.
[8] Ries C, Egea V, Karow M, et al. MMP-2, MT1-MMP, and TIMP-2 are essential for the invasive capacity of human mesenchymal stem cells: differential regulation by inflammatory cytokines. Blood. 2007;109(9): 4055-4063.
[9] Baek SJ, Kang SK, Ra JC. In vitro migration capacity of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells and their expression of a distinct set of chemokine and growth factor receptors. Exp Mol Med. 2011; 43(10):596-603.
[10] Fan H, Zhao G, Liu L, et al. Pre-treatment with IL-1beta enhances the eicacy of MSC transplantation in DSS-induced colitis. Cellular & Molecular Immunology. 2012;9(6):473-481.
[11] Sackstein R. The lymphocyte homing receptors: gatekeepers of the multistep paradigm. Curr Opin Hematol. 2005;12(6): 444-450.
[12] Karp JM, Leng Teo GS. Mesenchymal stem cell homing: the devil is in the details. Cell Stem Cell.2009;4(3):206-216.
[13] Xiao Q, Wang SK, Tian H, et al. TNF-α increases bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell migration to ischemic tissues. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2012; 62(3):409-414.
[14] Marquez-Curtis LA, Janowska-Wieczorek A. Enhancing the migration ability of mesenchymal stromal cells by targeting the SDF-1/CXCR4 axis. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:561098.
[15] Cao Z, Zhang G, Wang F, et al.Protective effects of mesenchymal stem cells with CXCR4 up-regulation in a rat renal transplantation model.PLoS One. 2013;8(12):e82949.
[16] Sackstein R, Merzaban JS. Ex vivo glycan engineering of CD44 programs human multipotent mesenchymal stromal cell trafficking to bone. Nat Med. 2008;14(2):181-187.
[17] Ridley AJ, Hall A. The small GTP-binding protein rho regulates the assembly of focal adhesions and actin stress fibers in response to growth factors. Cell. 1992;70(3): 389-399.
[18] Szczur K, Xu H, Atkinson S, et al. Rho GTPase CDC42 regulates directionality and random movement via distinct MAPK pathways in neutrophils. Blood. 2006;108(13): 4205-4213.
[19] Wang HS, Hung SC, Peng ST, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells in the Wharton’s Jelly of the Human Umbilical Cord. Stem Cells. 2004;22(7):1330-1337.
[20] Yao W, Guan M, Jia J, et al. Reversing bone loss by directing mesenchymal stem cells to bone.Stem Cells. 2013;31(9): 2003-2014.
[21] Garcia KO, Ornellas FL, Martin PK, et al.Therapeutic effects of the transplantation of VEGF overexpressing bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in the hippocampus of murine model of Alzheimer's disease. Front Aging Neurosci.2014;doi: 10.3389/fnagi.
[22] Brennen WN, Denmeade SR, Isaacs JT. Mesenchymal stem cells as a vector for the inflammatory prostate microenvironment. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2013;20(5): R269-290.
[23] 王更银,刘素蕊,赵春生.超顺磁性氧化铁标记脐带间充质干细胞后的活体MRI示踪[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2012; 16(36):6690-6695.
[24] Chen W, Li M, Yan ZL, et al. Effect of CXCR4 gene overexpression mediated by lentiviral vector on the biological characteristics of mesenchymal stem cells. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi.2013;34(5):440-444.
[25] Yellowley C. CXCL12/CXCR4 signaling and other recruitment and homing pathways in fracture repair.Bonekey Rep. 2013;2: 300.
[26] Ridley AJ. Rho GTPases and cell migration. J Cell Sci. 2001; 114(15):2713-2722.
[27] Brand AC, Morrison E, Milne S, et al.Cdc42 GTPase dynamics control directional growth responses.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111(2):811-816.
[28] He Y, Li D, Cook SL, et al.Mammalian target of rapamycin and Rictor control neutrophil chemotaxis by regulating Rac/Cdc42 activity and the actin cytoskeleton. Mol Biol Cell.2013; 24(21): 3369-3380.
[29] Ishihara D, Dovas A, Park H, et al. The chemotactic defect in wiskott-Aldrich syndrome macrophages is due to the reduced persistence of directional protrusions. PLoS One.2012;7(1): e30033.
[30] Heasman SJ, Ridley AJ. Mammalian Rho GTPases: new insights into their functions from in vivo studies.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008;9(9):690-701.
[31] Hou A, Toh LX, Gan KH, et al. Rho GTPases and regulation of cell migration and polarization in human corneal epithelial cells. PLoS One. 2013;8(10): e77107.
[32] Teo GS, Ankrum JA, Martinelli R. Mesenchymal stem cells transmigrate between and directly through tumor necrosis factor-α-activated endothelial cells via both leukocyte-like and novel mechanisms.Stem Cells. 2012;30(11):2472-2486.
[33] Reymond N, Im JH, Garg R,et al.Cdc42 promotes transendothelial migration of cancer cells through β1 integrin. J Cell Biol. 2012;199(4):653-668.
[34] Hong IK, Jeoung DI, Ha KS, et al.Tetraspanin CD151 stimulates adhesion-dependent activation of Ras, Rac, and Cdc42 by facilitating molecular association between β1 integrins and small GTPases. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(38): 32027-32039. |
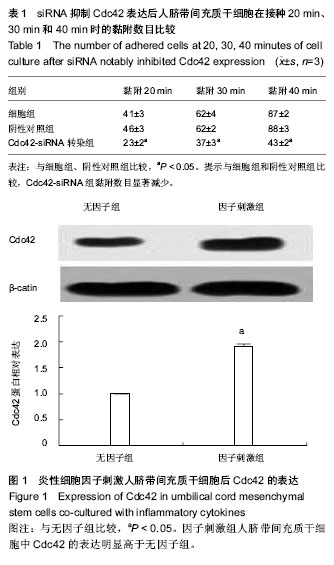
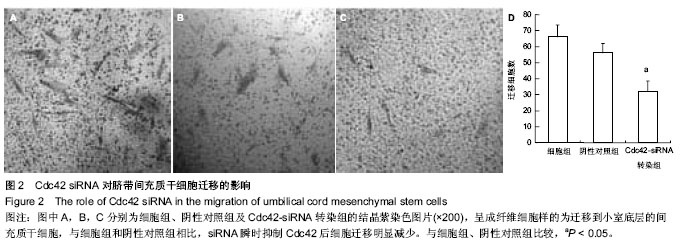
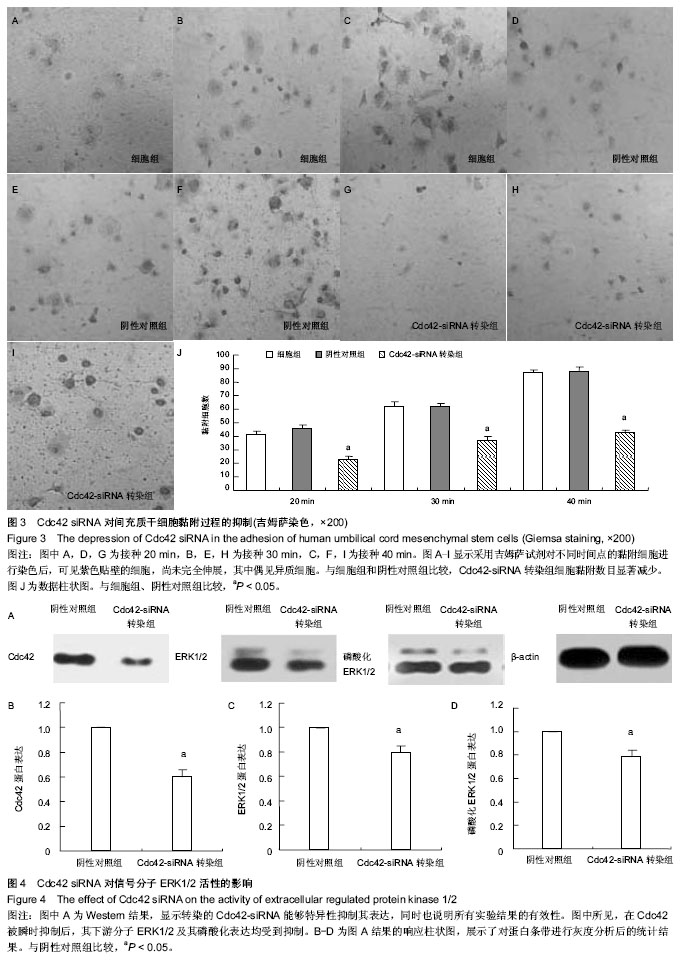
.jpg)